The topics in the cloud, above the line, constitute software engineering. The areas of
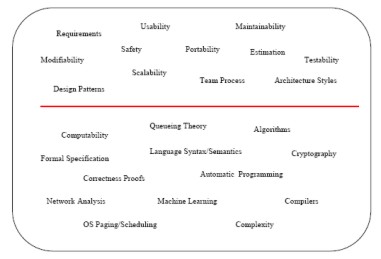
study in the cloud, below the line, are the core subjects of computer science.
A common question that students of this course ask is: “What is the difference between the various university courses: computer science, software engineering, computer engineering, electrical engineering, etc. ?” For every university there appears to be a different set of computer related options. What’s the difference between them?
The short answer, if you are only concerned with job prospects, is “Nothing”. All of them could easily allow you to get a job at Rim, Google, Microsoft or any computer / software company.
However, that doesn’t really help, as you do need to make a choice. Which one is right for you?
Computer Science
Computer science is generally about the theory of computation. It is largely theoretical, like mathematics. It includes many areas: theory of automata, system organization and logic design, formal languages and computability theory, programming, language design, etc. In computer science you design algorithms, mathematically figure out their efficiency, and write code.
Computer Science is not just about building computers or writing computer programs. Computer science is no more about building computers and developing software than astronomy is about building telescopes, biology is about building microscopes, and music is about building musical instruments. The solution of many computer science problems may not even require the use of computer: just pencil and paper. In fact, some problems in computer science have been solved before computers were even built. That said, computer science IS about building computers, writing computer programs, and much more.
Software Engineering
While CS is about writing code, software engineering is about thinking about writing code. Software engineering is more about people and products. Software engineers design, code and test large software projects. Graduates of software engineering programs should be able to work in groups; make presentations to technical and non-technical audiences; write coherent well-reasoned reports; and assess the social, technical, legal, and commercial implications of the products they help to create.
Computer Engineering
This is similar to software engineering in that it deals a lot with software design and testing of software. But it also deals with hardware. It’s like computer engineering in high school: you design, make and program hardware, such as a robot or circuit board. Areas of study could include communications, robotics, networks, power and energy, business, security, entertainment, etc.
Electrical Engineering
This is like computer engineering, but with an even more focus on hardware and not so much on software. Electrical engineers apply electronic and electromagnetic/ optical design principles to design, build and test all sorts of devices used in communication, data storage, robotics, power and energy, manufacturing, computing, security, entertainment, etc.
Tips for Success in University / College
- Talk to guidance: Now! (They can help clarify choices)
- Go to university open houses and info sessions: Now! (Forget what other people say and make up your own mind about the university or college)
- It’s okay and common to switch programs after the first year, so don’t stress too much about that choice. (Few people stick with the plans they made in grade 11 or 12. You never have to be stuck in a program you don’t want.)
- While at university / college:
- Go to every class / tutorial / seminar / lab (If you pay attention they will tell you all you need to know to get a good mark and your presence indicates to them that you are keen and interested in the course)
- Go see the professor to ask him / her some question (so that they will know who you are and that you are keen on the subject)
This list is not exhaustive, but provides an idea of what options graduates have and what they have gone on to do. Some options are more directly associated with a Computer Science degree than others.
- Air Traffic Controller
- Chief Information Officer
- Computer Hardware Designer
- Computer Scientist
- Database Developer
- Entrepreneur
- Internet Consultant
- Law Enforcement Officer
- Materials Researcher
- Meteorological Technician
- Optical Technician
- Robotics Consultant
- Security Systems Programmer
- Special Effects Director
- Teacher
- Video Game Developer
- Artificial Intelligence Designer
- Computational Physicist
- Computer Network Specialist
- Computer Support
- eCommerce Consultant
- Industrial Designer
- Internet Safety Analyst
- Light and Optics Specialist
- Materials Tester
- Mining Consultant
- Professor
- Safety Engineer
- Seismologist
- Special Effects Coordinator
- Technical Writer
- Web Page Developer
- Business Systems Analyst
- Computer Engineer
- Computer Programmer
- Computer Technology Analyst
- Electronics Technician
- Interface Designer
- IT Specialist
- Manufacturing Machine Designer
- Mathematician
- Network Administrator/Support
- Researcher
- Satellite Communications Consultant
- Software Designer
- Systems Analyst
- Telecommunication Consultant
Some of these career choices may require additional education or preparation in the form of graduate studies, internships or professional formative courses and exams. For a more in-depth description of some of the careers mentioned above visit the
National Occupational Classification website.